Transfer-matrix method (optics)
The transfer-matrix method is a method used in optics and acoustics to analyze the propagation of electromagnetic or acoustic waves through a stratified (layered) medium.[1] This is for example relevant for the design of anti-reflective coatings and dielectric mirrors.
The reflection of light from a single interface between two media is described by the Fresnel equations. However, when there are multiple interfaces, such as in the figure, the reflections themselves are also partially transmitted and then partially reflected. Depending on the exact path length, these reflections can interfere destructively or constructively. The overall reflection of a layer structure is the sum of an infinite number of reflections, which is cumbersome to calculate.
The transfer-matrix method is based on the fact that, according to Maxwell's equations, there are simple continuity conditions for the electric field across boundaries from one medium to the next. If the field is known at the beginning of a layer, the field at the end of the layer can be derived from a simple matrix operation. A stack of layers can then be represented as a system matrix, which is the product of the individual layer matrices. The final step of the method involves converting the system matrix back into reflection and transmission coefficients.
Contents |
Formalism for electromagnetic waves
Below is described how the transfer matrix is applied to electromagnetic waves (for example light) of a given frequency propagating through a stack of layers at normal incidence. It can be generalized to deal with incidence at an angle, absorbing media, and media with magnetic properties. We assume that the stack layers are normal to the 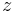 axis and that the field within one layer can be represented as the superposition of a left- and right-traveling wave with wave number
axis and that the field within one layer can be represented as the superposition of a left- and right-traveling wave with wave number 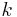 ,
,
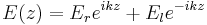 .
.
Because it follows from Maxwell's equation that 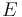 and
and 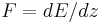 must be continuous across a boundary, it is convenient to represent the field as the vector
must be continuous across a boundary, it is convenient to represent the field as the vector 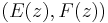 , where
, where
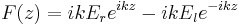 .
.
Since there are two equations relating 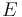 and
and 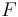 to
to 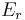 and
and 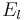 , these two representations are equivalent. In the new representation, propagation over a distance
, these two representations are equivalent. In the new representation, propagation over a distance 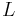 into the positive
into the positive 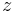 direction is described by the matrix
direction is described by the matrix
and
Such a matrix can represent propagation through a layer if 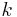 is the wave number in the medium and
is the wave number in the medium and 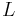 the thickness of the layer: For a system with
the thickness of the layer: For a system with 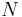 layers, each layer
layers, each layer 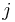 has a transfer matrix
has a transfer matrix 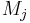 , where
, where 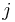 increases towards higher
increases towards higher 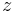 values. The system transfer matrix is then
values. The system transfer matrix is then
Typically, one would like to know the reflectance and transmittance of the layer structure. If the layer stack starts at 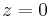 , then for negative
, then for negative 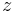 , the field is described as
, the field is described as
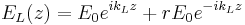 ,
,
where 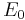 is the amplitude of the incoming wave,
is the amplitude of the incoming wave, 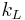 the wave number in the left medium, and
the wave number in the left medium, and 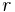 is the amplitude (not intensity!) reflectance coefficient of the layer structure. On the other side of the layer structure, the field consists of a right-propagating transmitted field
is the amplitude (not intensity!) reflectance coefficient of the layer structure. On the other side of the layer structure, the field consists of a right-propagating transmitted field
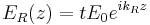 ,
,
where 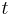 is the amplitude transmittance and
is the amplitude transmittance and 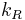 is the wave number in the rightmost medium. If
is the wave number in the rightmost medium. If 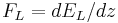 and
and 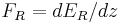 , then we can solve
, then we can solve
in terms of the matrix elements 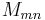 of the system matrix
of the system matrix 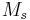 and obtain
and obtain
and
![r = \left[\frac{ (M_{21} %2B k_L k_R M_{12}) %2B i(k_L M_{22} - k_R M_{11})}{(-M_{21} %2B k_L k_R M_{12}) %2B i(k_L M_{22} %2B k_R M_{11})}\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/c2b80d87acecf4326c76f2c306647624.png) .
.
The transmittance and reflectance (i.e., the fractions of the incident intensity 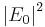 transmitted and reflected by the layer) are often of more practical use and are given by
transmitted and reflected by the layer) are often of more practical use and are given by 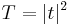 and
and 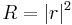 , respectively.
, respectively.
Example
As an illustration, consider a single layer of glass with a refractive index n and thickness d suspended in air at a wave number k (in air). In glass, the wave number is 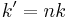 . The transfer matrix is
. The transfer matrix is
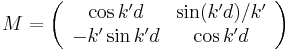 .
.
The amplitude reflection coefficient can be simplified to
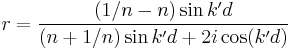 .
.
This configuration effectively describes a Fabry–Pérot interferometer or etalon: for 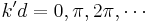 , the reflection vanishes.
, the reflection vanishes.
Acoustic waves
It is possible to apply the transfer-matrix method to sound waves. Instead of the electric field E and its derivative F, the displacement u and the stress 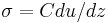 , where
, where 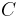 is the p-wave modulus, should be used.
is the p-wave modulus, should be used.
Abeles matrix formalism
The Abeles matrix method is a computationally fast and easy way to calculate the specular reflectivity from a stratified interface, as a function of the perpendicular momentum transfer, Qz.
Application
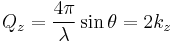
Where θ is the angle of incidence/reflection of the incident radiation and λ is the wavelength of the radiation. The measured reflectivity depends on the variation in the scattering length density (SLD) profile, (ρ(z)) perpendicular to the interface. Although the scattering length density profile is normally a continuously varying function, the interfacial structure can often be well approximated by a slab model in which layers of thickness (dn), scattering length density (ρn) and roughness (σn,n+1) are sandwiched between the super- and sub-phases. One then uses a refinement procedure to minimise the differences between the theoretical and measured reflectivity curves, by changing the parameters that describe each layer.
In this description the interface is split into n layers. Since the incident neutron beam is refracted by each of the layers the wavevector, k, in layer n, is given by:
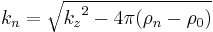
The Fresnel reflection coefficient between layer n and n+1 is then given by:
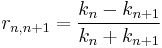
Since the interface between each layer is unlikely to be perfectly smooth the roughness/diffuseness of each interface modifies the Fresnel coefficient and is accounted for by an error function, as described by Nevot and Croce (1980).
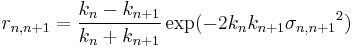
A phase factor, β is introduced, which accounts for the thickness of each layer.
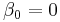
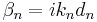
where 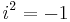 . A characteristic matrix, cn is then calculated for each layer.
. A characteristic matrix, cn is then calculated for each layer.
![c_{n}=\left[\begin{array}{cc}
\exp\left(\beta_{n}\right) & r_{n,n%2B1}\exp\left(\beta_{n}\right)\\
r_{n,n%2B1}\exp\left(-\beta_{n}\right) & \exp\left(-\beta_{n}\right)\end{array}\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/7b269715973d851c1449574bf9e81d5c.png)
The resultant matrix is defined as the product of these characteristic matrices
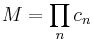
from which the reflectivity is calculated
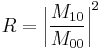
See also
References
- ^ Born, M.; Wolf, E., Principles of optics: electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light. Oxford, Pergamon Press, 1964.
Abeles matrix formalism
- O. S. Heavens. Optical Properties of Thin Films. Butterworth, London (1955).
- L. Nevot, P. Croce, Revue de physique appliquée, 15, 761 (1980).
- F. Abeles, Le Journal de Physique et le Radium, "La théorie générale des couches minces", 11, 307–310 (1950).
External links
Derivations and explanations
- Lecture notes by Bo Sernelius, see Lecture 13. This derivation is more general than the one above, including light that is incident at a non-normal angle, and with specific light polarizations.
Computer programs
There are a number of computer programs that implement this calculation:
- FreeSnell is a stand-alone computer program that implements the transfer-matrix method, including more advanced aspects such as granular films.
- Thinfilm is a web interface that implements the transfer-matrix method, outputting reflection and transmission coefficients, and also ellipsometric parameters Psi and Delta.
- Luxpop.com is another web interface that implements the transfer-matrix method.
- Transfer-matrix calculating program, written in Mathematica.
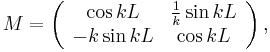
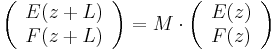

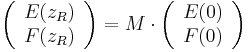
![t = 2 i k_L e^{-i k_R L}\left[\frac{M_{11} M_{22} - M_{12} M_{21}}{-M_{21} %2B k_L k_R M_{12} %2B i(k_R M_{11} %2B k_L M_{22})}\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/df49d7767c0131f7ed061aba3c0b5105.png)